The COVID-19 pandemic gives new relevance to a synthetic substance developed by Stanford researchers that could help respiratory patients breathe easier.
Author: Bruce Goldman
Brain imaging for stroke patients dropped off during COVID-19 height
In U.S. hospitals, the frequency of brain imaging for acute stroke patients dipped, suggesting hesitancy to seek medical care for non-COVID-19 conditions.
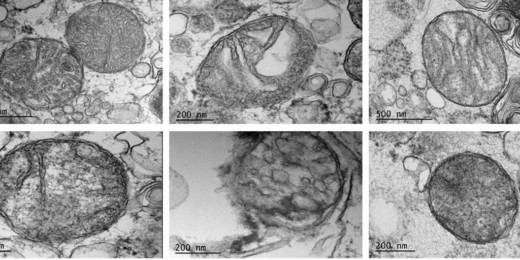
How chloroquine, coronavirus duke it out inside a dish
Even if chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine don't end up being the best treatment for COVID-19, observing how they work in a dish can teach scientists a lot.
Gel smooths cells’ ride through syringes in regenerative therapy
An innovative stem cell delivery method vastly improves the viability of tissue regenerating cells in animal spinal-cord injury models.
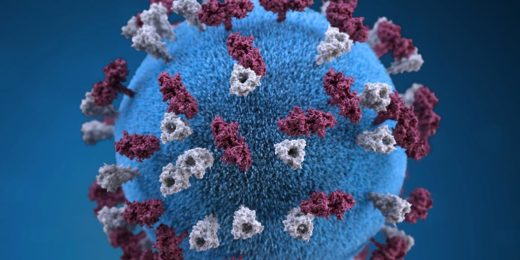
What’s a virus, anyway? Part 2: How coronaviruses infect us — and how viruses created us
A look at how viruses — including coronavirus — enter cells, use their molecular machinery to copy themselves and escape. And how to stop them.
What’s a virus, anyway? Part 1: The bare-bones basics
Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, viruses are getting a lot of attention; here's an inside look into the most abundant life form on Earth.
Macular degeneration steals sight. A chip implant may get it back.
In a clinical trial, a tiny prosthetic retinal device invented by a Stanford researcher has proved its potential ability to restore eyesight to the blind.
Identification of “missing microbe” spurs clinical trial in ulcerative colitis
A study links ulcerative colitis to the depletion of important acids ordinarily produced by a set of gut microbes mysteriously missing in action.
When things go wrong with mitochondria
Cellular respiration has a downside: Its byproducts harm the mitochondria that perform this trick, endangering our brain cells.
Suspicion: Why are virus-targeting immune cells sniffing around Alzheimer’s patients’ brains?
A new study has identified T cells targeting the Epstein-Barr virus in autopsied Alzheimer's brains and in cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer's patients.
Can Ecstasy be repurposed to catalyze the patient/psychotherapist bond?
Stanford researchers have teased apart the addictive and pro-social effects of MDMA -- suggesting the possibliity of a non-addictive therapy.
Why we talk with our hands — and how that may help give speech to the speechless
Stanford researchers found that the same part of the motor cortex that controls hand movement also appears to influence muscles used for talking.
How estrogen cycles change female mice’s (and possibly people’s) brains, governing sexual receptivity
A discovery about how a neural circuit located deep in the brains of female mice changes in response to estrogen could offer insight into human brains.
“Two Minds” two years later: Still curious about sex differences in cognition? Here are some resources
A Stanford Medicine magazine article on sex differences in the brain remains popular; this article provides additional information.
Why even well-controlled epilepsy can disrupt thinking
New research suggests why people with epilepsy, even when their seizures are well controlled, report lapses in their ability to think, perceive or remember.
Potential diagnostic, hope for a Parkinson’s disease treatment
A new discovery could provide a way of detecting Parkinson's disease in its earliest stages, before symptoms start. And it could accelerate the development of …