Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is caused by various genetic mutations that cause heart muscle to contract with too much force. New research suggests why.
Author: Bruce Goldman
On/off sociability switch in brain identified, could play a role in autism
An electrochemical on/off switch in the brain may spell the difference between sociability and social awkwardness, scientists have learned.
“Mood mirror” in blood: Might its absence bring on the blues?
Low levels of a substance, acetyl-L-carnitine, in the blood are associated with depression. Could this "mood mirror" be a cure for the blues?
How you get around depends on how fast you’re moving
How our brains blend cues from multiple senses to estimate our speed and position in space depends on where we are and how fast we seem to be moving.
Stitching single cells together any which way you want to
What if you could stitch together single cells any way you wanted to? Potential medical and even industrial applications abound.
The beating brain: A video captures the organ’s rhythmic pulsations
A group of researchers have developed an imaging method to show the brain in motion.
Why nicotine-mimicking molecules might make great anti-inflammatory drugs for MS, RA, gout and more
A set of structurally similar proteins can activate a receptor for nicotine on immune cells, resulting in a dialing down of inflammation.
Stanford psychiatrist, engineer and neuroscientist Karl Deisseroth wins 2018 Kyoto Prize
Stanford's Karl Deisseroth has won the 2018 Kyoto Prize in applied technology for his invention and application of optogenetics.
Lay off the laxatives — even a short bout of diarrhea can ruin your gut microbes’ month
In each of our abdomens sit trillions of microbes, but a bout of diarrhea can induce a lasting round of gut-bug disruption, new research indicates.
Huge study shows cancer benefits, limitations of antiretroviral therapy for HIV
Antiretroviral therapy, a breakthrough treatment for HIV infection, suppresses the levels of circulating HIV viral particles in the blood. When it works, cancer rates drop, according to a new study. Still, even when the therapy is successful, HIV-positive individuals retain elevated rates of cancer.
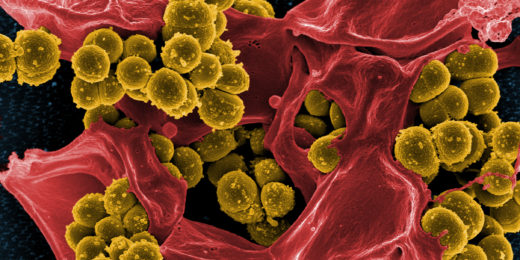
Bad bug’s Achilles heel: New drug targets identified for S. aureus
A hitherto unheralded set of telltale enzymes may prove to be perfect targets for shooting down a gang of nasty bacterial pathogens collectively called S. aureus.
Found in a mouse: the brain’s “face your fear” center
The discovery, in mice, of a pair of nerve clusters regulating fearful versus bold responses to a visual threat could help people with excessive anxiety, phobias or post-traumatic stress disorder lead more normal lives.
Breathing easy: Synthetic lung surfactant could save lives, at low cost
What makes breathing possible is a thin coating of a soaplike film, or surfactant, that lowers the tension of the lung’s inner surface. Premature babies and adults with lung injuries are short on surfactant, and replacing it has been prohibitively pricey. That may be about to change.
Tackle opioid addictions at the onset, the doctor’s office, Stanford researchers urge
In a JAMA opinion piece, Gary Peltz and Tom Sudhof argue for policymakers and health leaders to combat opioid addictions early.
Older people’s immune cells get fuzzier marching orders than those of younger people
Older people are more susceptible to infection, cancer, and autoimmunity than younger people. This may be the result of our immune cells' receiving increasingly random marching orders as we age.
Being a neuroscientist: A conversation with veteran Stanford brain researcher Rob Malenka
In an interview in the journal Neuron, Stanford's Rob Malenka holds forth on a wide range of subjects stretching from reflections on his own career trajectory to his approach to boosting those of his trainees to the future of neuroscience itself.