Scientists who work with the Stanford Precision Health and Integrated Diagnostics Center set out to find new ways to precisely predict, prevent and diagnose diseases that range from diabetes to mental health.
Author: Hanae Armitage
The digital evolution of health care at Big Data in Precision Health
During a digital health-focused session at the Big Data in Precision Health conference, four speakers detailed the ways in which they're harnessing digital technologies to empower patient health.
Elevating everyone at the Big Data in Precision Health conference
Experts from academia, industry government and more came together at this year's Big Data in Precision Health conference to share successes, lessons and insights into how they're breaking down data to precisely advance health care and research.
What everyone should know about HPV
During a recent talk, Lisa Goldthwaite, a clinical assistant professor at Stanford, told the truths of HPV, sharing practical insights and lessons that are important to everyone's health.
Contraception: An evolution and history
At the recent Stanford Women's Health Forum, Kate Shaw, a clinical associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology, spoke about the evolution and history of birth control.
Countdown to Big Data in Precision Health: Understanding the hype and the hope for AI in health care
Dekel Gelbman, CEO of FDNA, speaks on the role of artificial intelligence in health care, and how he sees AI contributing to genetic diagnostic in particular.
PET scan tracer could predict efficacy of cancer “vaccine”
Scientists at Stanford have created a new PET scan-compatible tracing agent that tracks immune cells poised to attack cancer, offering a new way to predict the success of certain therapies.
Countdown to Big Data in Precision Health: Where machine learning and clinical care intersect
Jenna Wiens, an assistant professor at the University of Michigan, speaks to how big data, machine learning and health care intersect in advance of the Big Data in Precision Health conference at Stanford.
New “MAGESTIC” gene-editing technology makes precise changes to millions of cells at once
A new gene-editing technology enables scientists to make thousands of edits at once and track them with specific barcodes.
Countdown to Big Data in Precision Health: Breaking down data to improve health care
Jennifer Schneider, chief medical officer, breaks down her perspective on the intersection of technology and health care in preparation for this year's Big Data in Precision Health conference.
UK Biobank data opens up window into genetics of disease
A biobank from the U.K. releases hundreds of thousands of anonymized medical records and genetic data to scientists, who used it to track down new links between genetics and disease.
Countdown to Big Data in Precision Health: Venture capital in health care
Lisa Suennen of GE Ventures speaks about big data and digital innovations in the month leading up to her talk at Stanford's Big Data conference.
Using CRISPR to edit coral
In a proof-of-principle study, Stanford scientists and colleagues used the CRISPR/Cas9 system to modify genes in coral, suggesting that the tool could one day aid conservation efforts.
Making moves to increase diversity in radiology — “It’s a must”
Stanford's Department of Radiology boosts its diversity effort, focusing on education, diversity in leadership and inclusion.
It’s time to abandon the term “obesity paradox,” Stanford researchers say
Scientists argue that using the term "obesity paradox" to describe situations in which obese patients have unexpectedly better health outcomes is actually a disservice to scientific advancement.
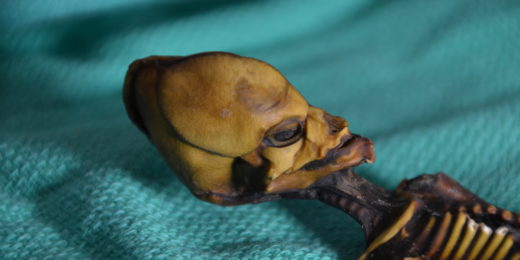
Bizarre skeleton sheds light on mutations of bone disease
The strange skeletal remains of a fetus discovered in Chile have turned up new insights into the genetics of some bone diseases, according to a new study.