The ultimate goal: a vaccine with coverage so broad it can protect against viruses never before encountered.
Category: Animal Research
Scientists identify ‘Velcro-like’ molecule to potentially treat ALS
A drug created by Stanford Medicine scientists aimed at a ‘Velcro’-like protein reduces ALS symptoms and improves survival in mice.
Restoring the blood-brain barrier?
Stanford Medicine scientists and collaborators discover a treatment in mice to repair the blood-brain barrier, which is key to brain health.
Runaway immune reactions cause long COVID breathing problems
Researchers at Stanford Medicine have investigated the mechanism of pulmonary fibrosis caused by long COVID.
Machine learning could enable faster, less costly epilepsy drugs
Researchers created an algorithm to determine if mice have epilepsy and whether they have been treated with seizure drugs.
Looking for love in all the wrong hormones
Researchers have found that oxytocin, commonly known as the "love hormone" may not be crucial for the social behaviors it's known for.
A big jump in prosthetic vision
By devising special pixels, Stanford University researchers have enhanced prosthetic vision with a new implant that improves vision.
Wireless implant could help remove deadly brain tumors
Brain tumors are among the most deadly and difficult-to-treat cancers. Glioblastoma, a particularly aggressive form, kills more than 10,000 Americans a year and has a …
What can squid brains teach us about nervous system evolution?
Researchers are studying the bobtail squid to learn more about the evolution of intelligence. Their focus is on "large genes."
Can we rejuvenate aging brains?
A Stanford Medicine researcher discusses his neuroscience-driven investigation into aging and if it's possible to rejuvenate an aging brain.
Losing sleep in adolescence makes mice less outgoing as adults
Mice that had sleep interruptions during adolescence had less interest in making new friends later on, a Stanford study shows.
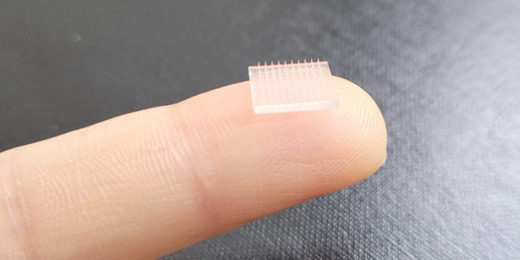
A new approach to vaccinations: 3D printed patches
Researchers have created a new prototype technology to administer vaccines: a 3D printed patch that packs a punch.
Clues from Down syndrome hint at new Alzheimer’s finding
Researchers at Stanford Medicine have discovered a possible molecule connection between Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease.
Cone snail venom and … insulin?
People with diabetes must plan meals and insulin doses, a hassle that may one day be eliminated thanks to cone snail venom.
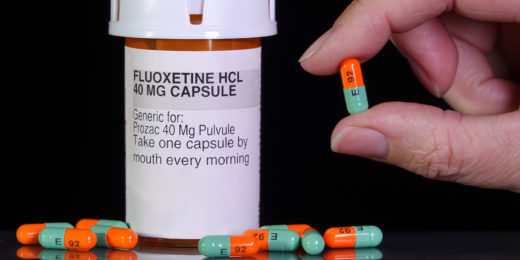
Can Prozac fight brain cancer?
The common antidepressant Prozac melts away glioblastoma tumors in laboratory mice, suggesting possible treatment for the deadly cancer.
Tracking the progression of liver disease in a dish
Stanford Medicine researchers are creating models of livers in a dish -- organoids -- to better understand liver disease.