Often misunderstood and undertreated, bipolar disorder has received close attention from Stanford Medicine clinicians and researchers for more than 30 years.
Category: Cellular & Molecular Biology
Unconventional Paths: How she flipped traditional genomics analysis on its head
Statistics expert Julia Salzman returned to biology and has married her two areas of expertise to design a new form of genomics analysis.
Going beyond B cells in the search for a more multi-targeted vaccine
The ultimate goal: a vaccine with coverage so broad it can protect against viruses never before encountered.
Searching for vaccine variability in the land of the flu
The ultimate goal: a vaccine with coverage so broad it can protect against viruses never before encountered.
The hunt for a vaccine that fends off not just a single viral strain, but a multitude
Stanford Medicine researchers are designing vaccines that might protect people from not merely individual viral strains but broad ranges of them. The ultimate goal: a vaccine with coverage so broad it can protect against viruses never before encountered.
The human lipidome reveals new indicators of health, disease and aging
A new survey of an under-explored aspect of human biology uncovers the many roles of the body’s “greasy molecules.”
A more complete imaging technique could personalize cancer treatment
Stanford Medicine scientists devised a cancer imaging technology that opens doors to new research questions and precision medicine.
mRNA vaccine spike protein differs from viral version
Scientists explain a key difference between the spike-protein molecules generated by the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine and those the virus induces.
How an ultra-sensitive on-off switch helps axolotls regrow limbs
Stanford Medicine researchers discover an "on-off" switch that powers tissue regeneration in axolotls, a type of salamander.
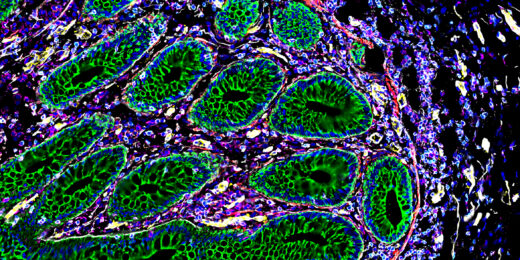
It’s a beautiful day in the intestinal neighborhood
Researchers have mapped the human intestine at the level of individual cells, showing how cellular neighborhoods work together in the gut.
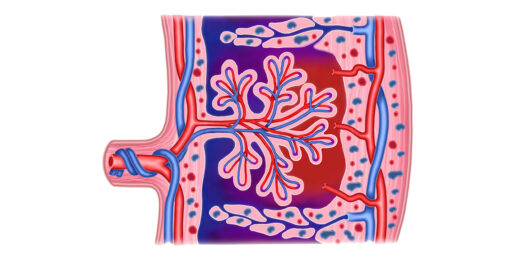
Stanford Medicine researchers map morphing placenta
Researchers at Stanford Medicine have created a detailed map of how cells in the placenta change during pregnancy.
Ribosomes’ sweet spot
Researchers at Stanford Medicine discover an unknown quirk about the ribosome and make a sweet representation along the way.
Special delivery 2.0: CARTs
Researchers at Stanford are devising new ways to deliver mRNA to the body to facilitate more potent and accurate treatments and vaccines.
Special delivery – an mRNA explainer
This is Part I in a series that will explore the promise, challenges and future of mRNA. Let's count our blessings. The COVID-19 pandemic, from …
Molecular movie maker
Researchers are harnessing an imaging technique called cryogenic electron microscopy to design drugs and better understand disease.
Stanford Medicine magazine explores the molecules within us
Stanford Medicine magazine explores the molecules behind human biology and how understanding them fuels medical discoveries and innovations.