Stanford Medicine cognitive neuroscientists show that a brain imaging tool with real-time feedback helps children with ADHD perform tasks that require working memory.
Author: Erin Digitale
What COVID-19 taught us about protecting kids in future pandemics
Stanford Medicine infectious disease expert Yvonne Maldonado leads calls to ensure children are top of mind in preparing for future pandemics.
Stanford Medicine experts help Nobel winner custom design proteins for COVID-19 therapy
Custom designing proteins — a breakthrough recognized by the latest Nobel Prize in chemistry — could yield treatments that stop the worst of COVID-19 before it begins.
California excels at screening babies for main cause of childhood blindness
Vision damage from a complication of premature birth can be halted if it’s caught soon enough — and a California Perinatal Quality Care (CPQCC) and Stanford Medicine-led study shows the state’s screening process is helping close racial gaps.
The inflammation connection: Kids with PANS at high risk for arthritis
‘We’re like inflammation detectives!’ says Stanford Medicine’s Jennifer Frankovich. Parsing out pain and inflammation is just part of discovering why kids face debilitating psychiatric effects of a distressing disease.
How gaps in pediatric obesity treatment make access inequitable
Thomas Robinson wrote an editioral about the new guidelines, outlining what treatments got the top recommendation, and how gaps in the healthcare system make access to the best treatments inequitable.
Mental health and menopause: There are connections and solutions
Many women experience extreme mood fluctuations as they approach menopause. Stanford Medicine’s Karen Adams says knowledge and access are key to aiding this normal condition.
In the age of fentanyl, factual drug education can save teen lives
Toolkits designed by Stanford Medicine researchers are helping teens think critically about the choices they make around substance use these days, from tobacco to cannabis to pills that could contain fentanyl.
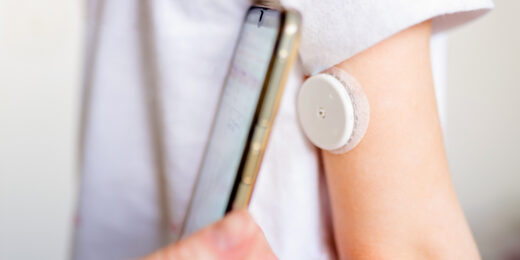
These are the tools for providing top-notch diabetes care to everyone
Using AI, continuous glucose monitors, and an equity approach, diabetes care could be saving many more lives, Stanford Medicine researchers say.
What getting granular with pregnancy data means for those of AANHPI heritage
By further segmenting study results, Stanford Medicine’s Irogue Igbinosa and collaborators have begun to tease out important health differences between different subsets of the population.
Inequity of genetic screening: DNA tests fail non-white families more often
Research is showing that advanced methods of genetic testing aren’t equally useful for everyone: They’re less accurate for non-white families, raising concerns about how historical gaps in whose DNA gets studied produce inequities in medical care.
Why precision medicine’s targeted interventions may help prevent dangerously early births
Approximately 10% of babies worldwide are born three or more weeks before their due date -- making premature birth the leading cause of death for children under 5 globally.
How California is taking on inequity for Black patients during pregnancy, childbirth
Across the United States, Black women are three to four times as likely as their white peers to experience life-threatening pregnancy complications or die giving birth
More kids are being hospitalized for eating disorders — researchers learned why
Over the last decade, physicians have taken a broader view of adolescent eating disorders, thanks to a growing recognition of the variety of disordered eating patterns that can harm patients’ health, especially their heart function.
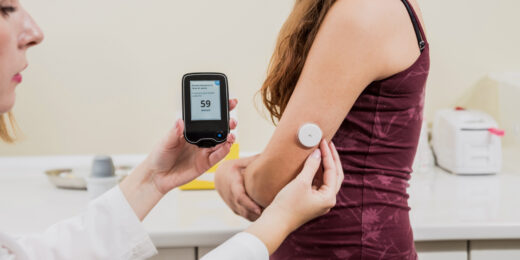
Why precision medicine leads to better diabetes care
Improvements in treatment technology are helping physicians deliver individualized care to their Type 1 diabetes patients.
No more ‘just deal with it’: Helping teens have easier periods
Nichole Tyson, MD, has advice for young people seeking help for menstrual problems – including painful, irregular or heavy periods.