Earlier this year, the largest tobacco company in the world paid millions to fund continuing medical education courses on nicotine addiction —16,000 physicians and other health care providers took them.
Author: Nina Bai
Could anesthesia-induced dreams wipe away trauma?
Cases of patients who recovered from trauma after dreaming under surgical anesthesia spur Stanford Medicine researchers to investigate dreaming as therapy.
Why detecting the earliest biological signs of Parkinson’s disease is so crucial
A new test can detect the biological signature of Parkinson’s disease before symptoms arise. A Stanford Medicine neurologist explains why early diagnosis opens the door to better therapies.
Match Day 101: How does the medical residency match work?
Graduating medical students go through an unusual springtime ritual known as Match Day to find out where they’ll continue their training. Here’s everything you wanted to know about the big day.
Why we should be fighting heart disease more like we fight cancer
Despite being the leading cause of death worldwide, heart disease feels less threatening than cancer and inspires less urgency in patients and providers. A Stanford cardiologist explains how we should react instead.
The human lipidome reveals new indicators of health, disease and aging
A new survey of an under-explored aspect of human biology uncovers the many roles of the body’s “greasy molecules.”
New AI tool for pathologists trained by Twitter (now known as X)
Stanford Medicine researchers create a new AI-powered algorithm that analyzes pathology images based on data from Twitter, now known as X.
Satisfaction with online dating app depends on what you’re looking for
A new study shows that some Tinder users access the the app to cope with negative emotions, but they may not find what they’re looking for.
Unconventional Paths: Rock climber turned trauma surgeon
Once a professional climber, Joe Forrester had a near-death experience that put him on a path to be a trauma surgeon at Stanford Medicine.
Binge eating linked to habit circuitry in the brain
People with binge eating disorders have differences in their brains’ habit circuitry, which may explain why these behaviors are so persistent.
How hypnosis can alter the brain’s perception of pain
Stanford Medicine physician David Spiegel, MD, explains how hypnosis can be effective against pain and why some people are more hypnotizable.
For better video meetings, try taking turns talking
Stanford Medicine scientists have identified how virtual interactions stilt our conversations and what that looks like in the brain.
Study counts mortality among doctors during pandemic
Despite more exposure to COVID-19, physicians experienced a lower excess mortality rate than Americans overall
New visions for mental health care
Researchers, policy makers, clinicians and others convened to discuss new approaches and innovations to improve mental health care.
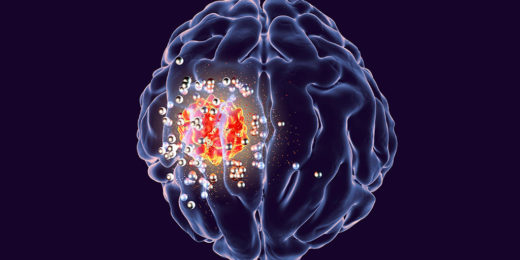
Wireless implant could help remove deadly brain tumors
Brain tumors are among the most deadly and difficult-to-treat cancers. Glioblastoma, a particularly aggressive form, kills more than 10,000 Americans a year and has a …
Do synchronized brains predict happy marriages?
Researchers found that couples who share similar brain activity while watching movie scenes about marriage report happier relationships.