A Stanford Medicine article examines CRISPR, the gene-editing technology, and addresses its potential to help with conditions such as sickle-cell disease.
Category: Genetics
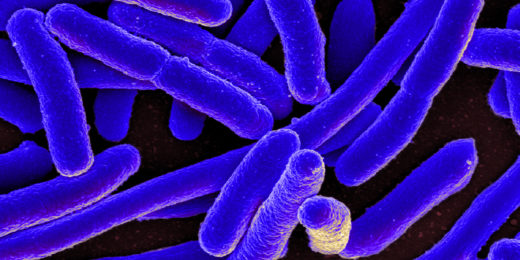
Big bacteria may be easier to kill, new research suggests
Stanford researchers have discovered a genetic "tuning knob" that can enlarge or shrink bacteria across a wide range - and this can be used to fatten up the bacteria to increase their susceptibility to certain antibiotics.
Aging neural stem cells struggle to take out the trash, say Stanford researchers
Protein aggregates in young neural stem cells seem to echo those seen in neurodegenerative disease-- but could they actually be helpful? As the cells age, they become less able to process the aggregates and their ability to activate is dampened.
The essence of precision health: Clinical Genomics Program to open at Stanford this spring
A new Clinical Genomics Program at Stanford will improve the diagnosis of rare genetic diseases, benefiting patients such as Tessa and Colton Nye.
CRISPR helps scientists track down potential therapeutic targets for ALS
Scientists have used genome editing to pinpoint genes that reveal information about ALS and may even protect against the degeneration of neurons.
Stanford Medicine magazine explores medicine’s new frontiers
Stanford Medicine magazine's winter issue explores science that pushes boundaries and also considers ethical questions raised about research.
Database allows physicians to tailor prescriptions to complement an individual’s genome
Stanford's Russ Altman discussed the pharmgkb.org database — which matches genomes with medication information — at the recent Beckman Symposium on campus.
Key genes for species diversity have been systematically ignored, Stanford study suggests
Researchers have assumed that "synonymous" mutations don't matter. Now it looks like they're among the most important for creating species diversity.
Men’s typically taciturn Y chromosomes tell colorful tale of conquests, expansions
There's nothing more macho than a Y chromosome. It not only confers maleness on its recipient but is handed down from one generation to the next pretty much stubbornly unchanged. …
Imaging study shows genetics and environment affect different parts of the brain
One of the oldest scientific debates is "nature versus nurture" -- do inherited traits or environmental factors shape who we are, and what we do? …
New genetic study: More evidence for modern Ashkenazi Jews’ ancient Hebrew patrimony
I hail from the so-called Ashkenazi branch of Jews, who account for the great majority of all Jews in the world today. Ashkenazis are distinguished …