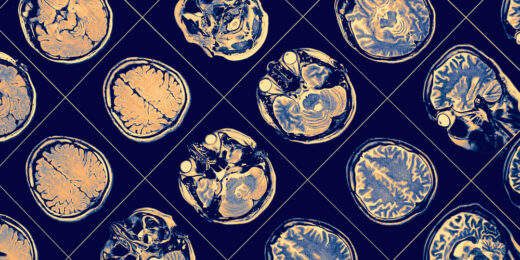
A few closely related drugs, all squarely aimed at treating Alzheimer’s disease, have served up what can be charitably described as a lackadaisical performance. Stanford Medicine neurologist Mike Greicius explains why these drugs, so promising in theory, don’t appear to be helping patients much if at all.
Author: Bruce Goldman
Going beyond B cells in the search for a more multi-targeted vaccine
The ultimate goal: a vaccine with coverage so broad it can protect against viruses never before encountered.
Searching for vaccine variability in the land of the flu
The ultimate goal: a vaccine with coverage so broad it can protect against viruses never before encountered.
The hunt for a vaccine that fends off not just a single viral strain, but a multitude
Stanford Medicine researchers are designing vaccines that might protect people from not merely individual viral strains but broad ranges of them. The ultimate goal: a vaccine with coverage so broad it can protect against viruses never before encountered.
mRNA vaccine spike protein differs from viral version
Scientists explain a key difference between the spike-protein molecules generated by the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine and those the virus induces.
Where in the brain is my sense of self?
Stanford Medicine researcher Josef Parvizi explores the neural origins of where one's sense of self lives in the brain.
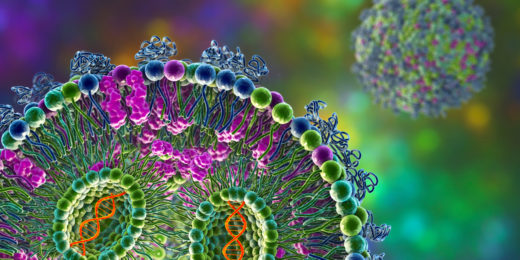
mRNA medicines: Looking back, and a look forward
Stanford Medicine experts discuss the past successes and future potential of mRNA as a new type of medicine or treatment.
Looking for love in all the wrong hormones
Researchers have found that oxytocin, commonly known as the "love hormone" may not be crucial for the social behaviors it's known for.
Special delivery 2.0: CARTs
Researchers at Stanford are devising new ways to deliver mRNA to the body to facilitate more potent and accurate treatments and vaccines.
Special delivery – an mRNA explainer
This is Part I in a series that will explore the promise, challenges and future of mRNA. Let's count our blessings. The COVID-19 pandemic, from …
Molecular makeover makes wimpy antibody a SARS-CoV-2 tackler
By harnessing an antibody most overlooked, researchers devise a new possible way to stop viruses, even as they evolve.
Mucus: Outtakes on a molecule of major significance
Researchers are making connections between the role of mucus and human health -- both in the brain and the lungs.
Can we rejuvenate aging brains?
A Stanford Medicine researcher discusses his neuroscience-driven investigation into aging and if it's possible to rejuvenate an aging brain.
Addictive potential of social media, explained
Stanford psychiatrist Anna Lembke’s book, Dopamine Nation, explains our brain chemistry's role in modern society's addiction to social media.
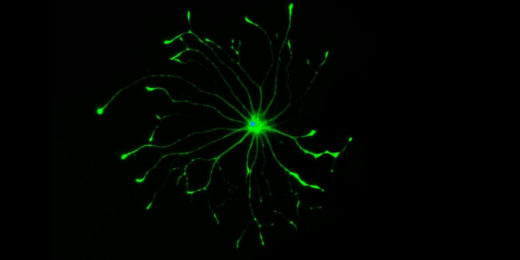
From angel to demon: Why some brain cells go ‘bad’
Four years after his death, possibly the greatest mystery famed neuroscientist Ben Barres ever sought to solve has become a bit less opaque.
Can major surgery increase risk for Alzheimer’s disease?
During cardiac surgery, patients’ blood levels of a substance highly predictive of Alzheimer’s disease jumped more than 5-fold.