Stanford scientists have figured out a way to convert common brewer’s yeast into an efficient factory for making a non-narcotic cough medicine that occurs naturally only in opium poppies.
Author: Bruce Goldman
Common link — a glucose-guzzling immune cell — involved in coronary artery disease and rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis and coronary artery disease share a common culprit: an important type of immune cell, called a macrophage, that has gone haywire. Stanford investigators have zeroed in on a molecular defect in macrophages' metabolic process that drives both disorders.
“Brain balls” let scientists mimic, study neurodevelopmental disorders in a dish
The human brain, and how it works, is one of the great mysteries of science. If only you could grow a brain in a bottle, you could learn a lot about what can go wrong – or for that matter, what goes right – in early brain development. So that's why Sergiu Pasca did.
Advanced cell-labeling technology identifies suspect cell type, possible new therapeutic approach to multiple sclerosis
Researchers have identified an immune cell type with an apparently critical role in multiple sclerosis, and a way to block its entry into the brain.
Coordinately altered protein/receptor combo could eliminate side effects of promising anti-cancer therapy
A promising anti-cancer therapy works great at first, but then loses its punch. A clever workaround may provide high-octane efficacy, without side effects.
Researcher’s crazy contraptions can simplify scientific complexities, distill research findings
Many infectious diseases are marked by cyclical ups and downs. Stanford's David Schneider takes a creative approach to making sense of them.
Defects in mitochondria, cells’ internal power packs, further linked to Parkinson’s in Stanford study
New research suggests that targeting mitochondria could be a way to treat Parkinson's disease.
Brainwide spread of seizures linked to specific cell type, new study shows
New Stanford Medicine research shows that a type of nerve cell called mossy cells play a key role in seizures in temporal lobe epilepsy.
Exercise elevates blood signature difference between people with, without chronic fatigue syndrome
A new study suggests that a blood test following exercise may be a good way to differentiate between people who have ME/CFS and people who don't.
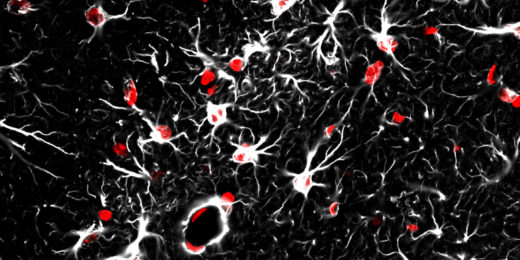
Star-shaped brain cells called astrocytes implicated in brain’s aging process, Stanford study shows
A new study led by the late Ben Barres suggests that rogue astrocytes may be involved in memory loss in otherwise healthy older brains.
Long-distance eye-brain connections, partial vision restored for first time ever in a mammal
The retina, a thin sheet of cells no more than half as thick as a credit card, is the light-sensing part of the eye. If nerve cells were …
Men’s typically taciturn Y chromosomes tell colorful tale of conquests, expansions
There's nothing more macho than a Y chromosome. It not only confers maleness on its recipient but is handed down from one generation to the next pretty much stubbornly unchanged. …
Stanford study: Commonly used sleeping pill may boost stroke recovery
If what works in mice works in people, a widely popular sleeping pill could someday start seeing action as an aid to stroke recovery, according …
New genetic study: More evidence for modern Ashkenazi Jews’ ancient Hebrew patrimony
I hail from the so-called Ashkenazi branch of Jews, who account for the great majority of all Jews in the world today. Ashkenazis are distinguished …
Mind-reading in real life: Study shows it can be done (but they’ll have to catch you first)
It's not a given that experimentally obtained results accurately reflect goings-on in the real world. The former are obtained under rigidly controlled, reproducible conditions in …
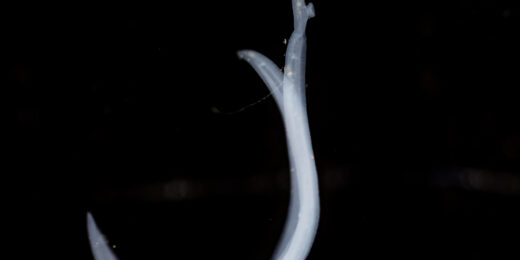
Is the worm turning? Early stages of schistosomiasis bladder infection charted
Think you've seen unattractive couples before? If you look up, you'll have the pleasure of viewing the ugliest couple you've ever seen: a male and …