Yetsa Adebodunde Tuakli-Wosornu, who wouldn’t be the person she is today without sports, led the charge for a new and improved International Olympic Committee consensus statement on interpersonal violence and safeguarding in sports.
Latest
Optimizing the telehealth experience could benefit patient, physician
Stanford Medicine's Kevin Schulman says digitally enabled care (DEC) would ease clinical workload and improve services for patients beyond virtual visits.
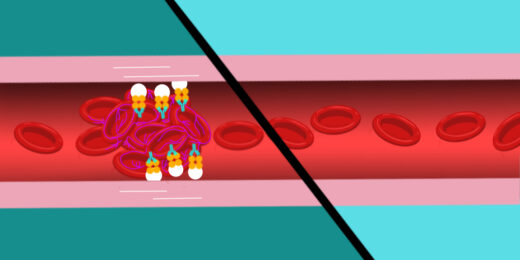
How this doctor is combatting a gravely serious clotting condition
Giselle Salmasi’s collaboration with a colleague at the Mayo Clinic gives a patient with a recently identified blood clotting disease a new lease on life.
Ask me anything: What to know about hearing loss
What actually causes hearing loss? Are there new treatments that can restore hearing? Can it be reversed? How does air travel affect hearing loss?
What’s the deal with BMI, aka body mass index?
Some researchers and clinicians are questioning the value of the body mass index, which estimates a person’s body composition. But do better alternatives exist?
Stanford Medicine launches new podcast, Health Compass
New Stanford Medicine podcast, Health Compass, focuses on the crucial research and important researchers moving health topics forward.
How supporting family, along with patients, became part of hospital’s mission
When the new Stanford Hospital opened five years ago, a carefully designed third-floor resource center gave for those caring for loved ones an important safe haven.
Biodesign cultivates community partnerships to broaden understanding of health equity
Biodesign program aims to ensure all trainees have a better understanding of health equity and appreciate the ways in which new technologies can widen or narrow the gaps in access to care.
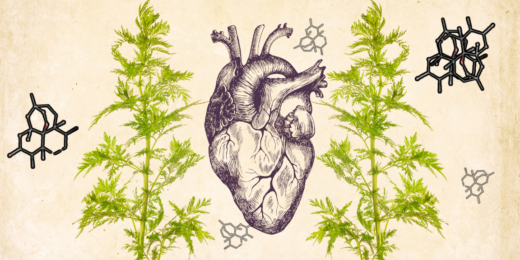
Old drug, new discovery: Scientists find novel use for ancient malaria remedy
Stanford Medicine researchers on the hunt for an elusive cardiac fibrosis drug were surprised when a malaria drug with ancient origins emerged as their top candidate.
A doctor, his cancer journey and a uniquely teachable moment
Bryant Lin has taken his diagnosis of stage IV ‘never-smoker’ lung cancer, which disproportionately affects those of Asian descent, and turned it into a medical school course. He hopes the world takes notes along with the students and Stanford Medicine community.
Stanford Medicine experts help Nobel winner custom design proteins for COVID-19 therapy
Custom designing proteins — a breakthrough recognized by the latest Nobel Prize in chemistry — could yield treatments that stop the worst of COVID-19 before it begins.
The cells that stoke the imaginations of Stanford Medicine scientists
Our researchers picked cells from all over the human body — cells of all shapes, sizes and abilities. From the brain to the heart to the intestines.
California excels at screening babies for main cause of childhood blindness
Vision damage from a complication of premature birth can be halted if it’s caught soon enough — and a California Perinatal Quality Care (CPQCC) and Stanford Medicine-led study shows the state’s screening process is helping close racial gaps.
From ballet to medicine, a love of stories has driven this bioethicist
Stanford Medicine bioethicist Tyler Tate found high levels of success in ballet, miming, acting, fencing and collegiate tennis. But his love of storytelling ultimately led him to medicine.
The new tech that could improve care for Parkinson’s patients
Technological advancements allow diabetes patients to monitor their glucose levels remotely. Stanford Medicine researchers are refining similar tools for Parkinson’s patients and the providers they don’t see often enough.
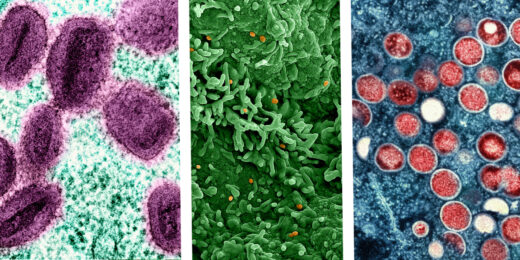
Understanding the resurgence of mpox
As a new form of the viral disease spreads through Central Africa, prompting a global emergency declaration, Stanford Medicine infectious disease specialist Abraar Karan discusses how health systems can prepare and respond.