With news cycles abuzz about the pros and cons of consuming seed oils, a nutrition expert breaks down what he believes consumers should know.
Category: Cardiology
Old drug, new discovery: Scientists find novel use for ancient malaria remedy
Stanford Medicine researchers on the hunt for an elusive cardiac fibrosis drug were surprised when a malaria drug with ancient origins emerged as their top candidate.
The cells that stoke the imaginations of Stanford Medicine scientists
Our researchers picked cells from all over the human body — cells of all shapes, sizes and abilities. From the brain to the heart to the intestines.
How space became a place for the study of aging
Stanford Medicine scientists are studying why even brief trips into space can weaken muscle and heart tissue, mimicking decades of aging on Earth.
Paying back her people: New doctor has plans to return to her African village
Bongeka Zuma, graduate of Oprah Winfrey’s academy and Stanford School of Medicine, discusses her plans to advance medical care in her hometown.
Researchers dial in on genetic culprit of disease
Genome-wide association studies can lay the groundwork to more precisely assess a person’s risk for disease, detect diseases earlier, reveal a molecular understanding of how certain illnesses arise, and point to new therapeutic targets.
New cardiovascular risk calculator includes social determinants of health, excludes race
Many social determinants of health can influence a patient’s risk, but Palaniappan and fellow researchers have noticed, from working with data from patients around the nation, that race is not among the most accurate or equitable.
Why we should be fighting heart disease more like we fight cancer
Despite being the leading cause of death worldwide, heart disease feels less threatening than cancer and inspires less urgency in patients and providers. A Stanford cardiologist explains how we should react instead.
More kids are being hospitalized for eating disorders — researchers learned why
Over the last decade, physicians have taken a broader view of adolescent eating disorders, thanks to a growing recognition of the variety of disordered eating patterns that can harm patients’ health, especially their heart function.
Is AI up to snuff? Cardiac clinical trial points to yes
Stanford Medicine researchers studied how AI can enhance evaluation of cardiac tests in the clinic and found it improved accuracy.
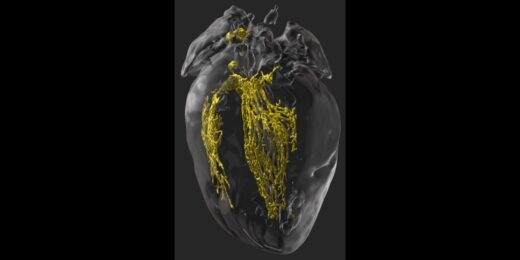
Making the invisible visible to improve heart surgery outcomes
Scientists find a way in mice to illuminate the cardiac conduction system during surgery to prevent unintended damage to healthy tissue.
Basic biochemistry research leads to heart-saving drug
Researchers at Stanford Medicine discovered the mechanism for a heart condition and developed a drug to treat it.
Unconventional Paths: Sneaky submarines and super surgeries
Bioengineer Alison Marsden uses computer modeling skills honed on submarines to help surgeons plan the best repairs for babies' hearts.
Unconventional Paths: Gorzynski and the great apes
After starting his career as a veterinarian, scientist John Gorzynski turned to research, investigating great ape genetics and cardiology.
How does CRISPR help researchers study the heart?
Cardiology researchers at Stanford Medicine are increasingly turning to CRISPR to understand -- and maybe one day -- treat heart disease.
Engineering a new heart, layer by layer
Stanford researchers are building a heart through tissue engineering techniques in the hopes of better treating congenital heart defects.