A Stanford neuroscientist has led the development of a novel brain research tool for understanding diseases of brain development.
Author: Bruce Goldman
Neuroscientist’s book traverses the extremes of human behavior
Stanford bioengineer, neuroscientist and psychiatrist Karl Deisseroth has written a new book -- and it’s not a ‘science book.’
Computer simulation may yield new COVID-19 drug
Stanford Medicine researchers have discovered a drug that could potentially be used to stave off SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
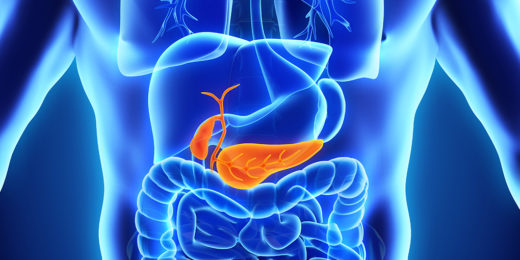
Coronavirus takes aim at insulin-producing cells in the pancreas
Stanford Medicine researchers discover that the virus behind COVID-19 attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
COVID-19 lab manager came to ‘where the fire is burning’
Obadia Mfuh Kenji joined Stanford after the pandemic's first surge in May 2020, overcoming challenges to help deploy COVID-19 testing.
Why C. diff wants to make you sick
Stanford research findings could lead to new ways to block the bacteria Clostridium difficile -- or C. diff -- from multiplying in our guts.
How long will a healthy older person live? A substance in blood may provide a clue
Blood levels of a brain-derived substance in people in their 90s and 100s accurately predict how much longer they're going to live.
Excised tonsils aid study of COVID-19 vaccines, the flu and more
Stanford scientists transformed tonsils into immunology labs in a dish, aiding research to develop vaccines for COVID-19, the flu and other diseases.
How do the new COVID-19 vaccines work?
The Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines are the first to use the RNA coding molecule to prompt our bodies to fight the virus. Here's how they work.
5 tips for safer voting during the COVID-19 pandemic
Planning to vote in person during the pandemic? Here's a list of practical steps to reduce your risk of coronavirus infection.
Clues about what makes SARS-CoV-2 tick (and how to stop it)
There's a voracious appetite for information on how SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, works. Here it is, in a single package.
What we can learn from COVID-19 in kids
A Stanford physician co-authored a list of likely biological factors underlying the reduced development of COVID-19 for children compared to adults.
Why the blood-brain barrier is really a filter, and what this means for the aging brain
Stanford-led research finds that the blood-brain barrier may be much more permeable -- albeit selectively so -- than previously thought.
High blood pressure drugs don’t increase COVID-19 risk, Stanford study finds
People taking two common types of drugs for hypertension are at no heightened risk, as has been feared, for increased severity or complications of COVID-19.
Enlisting the entire immune system strengthens potency of HIV vaccines in development
Two recent Stanford-led studies show the value of tweaking vaccines to enlist the entire immune system — not just part of it — in preventing HIV infection.
How remdesivir works, and why it’s not the ultimate coronavirus killer
How exactly does the antiviral drug remdesivir counter SARS-CoV-2 – the coronavirus strain responsible for COVID-19? And how well?