Helicobacter pylori, a potentially nasty bacteria, somehow lives in one of every two human stomachs -- no mean feat. Here's how the bug pulls it off.
Category: Infectious Diseases
Progress toward a universal flu vaccine
Stanford researchers have developed a technique to encourage the immune system to target a section of the flu virus that is conserved year to year.
Which blood-based method works best to detect TB?
Scientists at Stanford and beyond are working toward a new type of tuberculosis diagnostic that utilizes blood samples.
Paid family leave and health: A personal story and the latest research
A new policy brief from Stanford researchers identifies the connection between paid family leave and infant and maternal health benefits.
Partners-in-crime: Bacteria sics its pet virus on our immune cells to make us sick
P. aeruginosa, a type of bacteria, is increasingly drug-resistant, and there's no vaccine against it. But it has a recently discovered Achilles heel.
Mosquito tracking key to preventing disease outbreaks
Infectious disease expert Desiree LaBeaud is mapping outbreaks of Zika, dengue and chikungunya, three viral diseases transmitted by the same mosquitoes.
Treating parasite infections during pregnancy thought to boost babies’ immune responses
For babies in developing countries, pneumonia vaccines seem to work better if their mothers receive treatment for parasitic infections during pregnancy.
My measles story: The importance of protecting the most vulnerable
Writer Amy Adams reflects on her own experience with measles, and her lingering fears that she may have spread the virus to someone who was vulnerable.
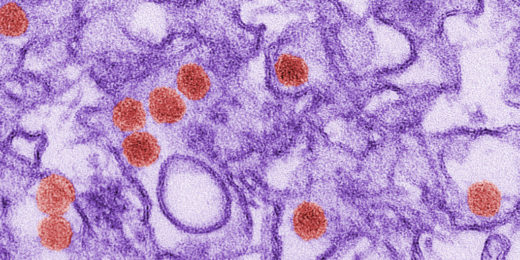
Blocking Zika: New antiviral may treat and prevent infection, a Stanford study suggests
A Stanford study shows Hsp70 protein inhibitors can protect mice from Zika virus without developing drug resistance, demonstrating their clinical potential.
When will dengue turn life-threatening? Researchers identify genes that provide a tell
Stanford scientists have devised a way to predict the severity of dengue cases using a set of 20 genes and specific expression patterns.
How yellow fever shaped 19th-century New Orleans: A Q&A
A Stanford historian explains how frequent yellow fever epidemics in 19-century Louisiana generated cultural and social norms in its fatal wake.
Mistaken identity: Influenza/narcolepsy autoimmunity link confirmed
New research has confirmed that an antigen in some variants of the flu virus and vaccine can, in rare cases, trigger an autoimmune response leading to narcolepsy.
Cholera and starvation in Yemen are preventable, Stanford pediatrician says
The civil war in Yemen has led to an cholera epidemic and widespread starvation. Both were preventable, Stanford pediatrician Paul Wise says.
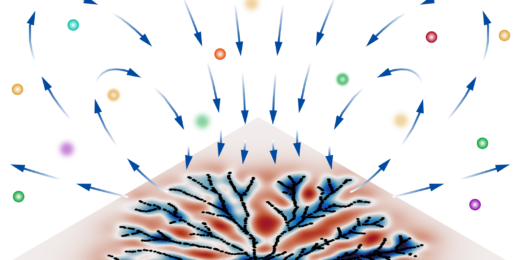
Biofilms feed with swirling flows
By learning more about the flows generated by a biofilm, researchers may discover new ways to cut off its supply of nutrients.
Health care financial burden of animal-related injuries is growing, study says
The cost of treating animal-related injuries in U.S. emergency rooms is about $1.2 billion per year, a new Stanford study shows.
Chemists shed light on Zika’s path to infection
New research examines how Zika viruses enter cells and shows that their behavior is different than that of some related viruses.