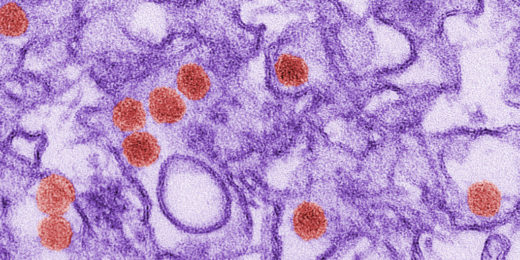
A Stanford study shows Hsp70 protein inhibitors can protect mice from Zika virus without developing drug resistance, demonstrating their clinical potential.
Category: Infectious Diseases
When will dengue turn life-threatening? Researchers identify genes that provide a tell
Stanford scientists have devised a way to predict the severity of dengue cases using a set of 20 genes and specific expression patterns.
How yellow fever shaped 19th-century New Orleans: A Q&A
A Stanford historian explains how frequent yellow fever epidemics in 19-century Louisiana generated cultural and social norms in its fatal wake.
Mistaken identity: Influenza/narcolepsy autoimmunity link confirmed
New research has confirmed that an antigen in some variants of the flu virus and vaccine can, in rare cases, trigger an autoimmune response leading to narcolepsy.
Cholera and starvation in Yemen are preventable, Stanford pediatrician says
The civil war in Yemen has led to an cholera epidemic and widespread starvation. Both were preventable, Stanford pediatrician Paul Wise says.
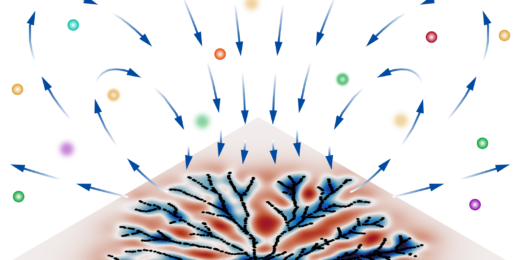
Biofilms feed with swirling flows
By learning more about the flows generated by a biofilm, researchers may discover new ways to cut off its supply of nutrients.
Health care financial burden of animal-related injuries is growing, study says
The cost of treating animal-related injuries in U.S. emergency rooms is about $1.2 billion per year, a new Stanford study shows.
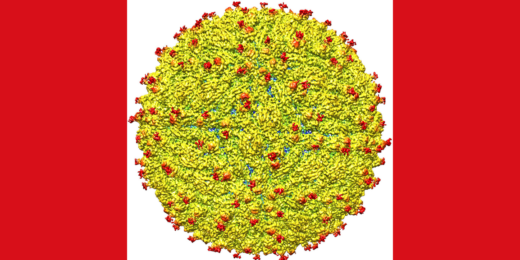
Chemists shed light on Zika’s path to infection
New research examines how Zika viruses enter cells and shows that their behavior is different than that of some related viruses.
Patients at high risk of HIV should take daily preventative drug, a task force recommends
The U.S. Preventative Services Task Force encourages those who are at high risk of contracting HIV to take a daily pre-exposure drug.
A new strategy for combatting antibiotic-resistant infections
Stanford chemists have developed a potential new strategy for fighting antibiotic-resistant bacterium — adding a new molecule onto an existing antibiotic.
100 years later, flu epidemic remains a possibility, Stanford physicians say
One hundred years after the 1928 influenza epidemic, flu remains a threat to society today, several Stanford emergency medicine clinicians explain.
Stanford scientist is working to halt spread of hepatitis B
Decision scientist Mehlika Toy is working with the WHO to help eliminate the public health burden of hepatitis B by the year 2030.
Inherited Neanderthal genes protect us against viruses, study shows
Stanford scientists have found that viral infections shaped human genome evolution after interbreeding with Neanderthals 50,000 years ago.
Immune cell ratios predict shift to active tuberculosis, Stanford-led study finds
The ratio between a certain types of immune cells is able to predict whether latent TB will shift into an active infection, new research has found.
New imaging technique can spot tuberculosis infection in an hour
A new imaging technology that harnesses fluorescence allows scientists to detect tuberculosis in an hour and to measure drug efficacy.
Cell membrane’s importance offers new strategy to fight infections
Found in about half of all bacterial species, the cell membrane that surrounds the cell wall may be more critical for survival than previously thought.