Researchers developed a novel way to image inflammation in multiple sclerosis, a disease that is notoriously difficult to diagnose early.
Category: Autoimmune Conditions
How hypnosis can alter the brain’s perception of pain
Stanford Medicine physician David Spiegel, MD, explains how hypnosis can be effective against pain and why some people are more hypnotizable.
Elite gastroenterologist’s path to being a champion of diversity
As an African American who also has a disability, Eric Sibley provides a role model for others within academic medicine.
I wrote a book about a scientist’s journey to save his desperately ill son
Stanford Medicine science writer Tracie White shares the origins of her new book that explores ME/CFS, family bonds, science, suffering, and much more.
Identification of “missing microbe” spurs clinical trial in ulcerative colitis
A study links ulcerative colitis to the depletion of important acids ordinarily produced by a set of gut microbes mysteriously missing in action.
Yes, it’s inflammatory bowel disease — but what kind? Soon it might be easier to tell
Diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease currently requires an invasive procedure. New research identifies a way to identify the disease using a blood draw.
Antibody treatment delays start of Type 1 diabetes by two years
A therapy delayed the onset of Type 1 diabetes in at-risk people by about two years, new results from a clinical trial show.
Sleep science takes the stage at Big Data in Precision Health
Speakers at Stanford's Big Data in Precision Health conference discuss how their work with big data impacts and informs sleep research.
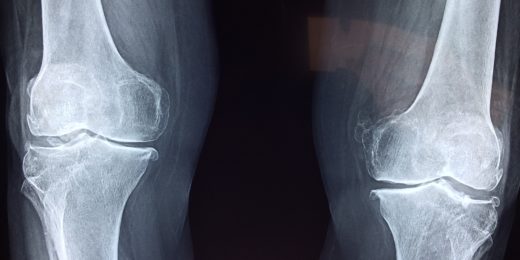
Immune-cell culprits fingered in osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis has traditionally been thought to be an inevitable result of wear and tear. But it's now clear the immune system is playing a leading role.
First diagnostic test for chronic fatigue syndrome identified
Inspired by his son's illness, Ron Davis and colleagues have discovered a diagnostic test for chronic fatigue syndrome, a notoriously elusive disease.
How drug-resistant bugs grow in CF patients’ lungs
Some viruses help drug-resistant bacteria grow in the lungs of cystic fibrosis patients, new Stanford research shows.
A cell’s “self-destruct” function could yield new therapies
Scientists studying cell death are working to understand how the body protects itself from disease and use that information to form better treatments.
Preventing osteoarthritis, an orthopaedic surgeon’s goal
Orthopaedic surgeon Constance Chu has spent her career seeking ways to prevent osteoarthritis from developing after a knee injury.
Type 1 diabetes: Developing an early warning system
Type 1 diabetes starts out as a sneak attack by bad-actor antibodies. But scientists at Stanford and UCSF have developed an early-warning system.
Rheumatoid arthritis may be triggered by a missing molecular “anchor,” but new research suggests a fix
Stanford scientists have dug up a defect at the heart of rheumatoid arthritis: a faulty "anchor" that should be tethering a key molecule to the spot inside immune cells where it has to be in order to do its job. It seems this defect can be reversed with a not yet commercially available small-molecule drug.
Physician-scientist’s “indomitable spirit” prevails over personal adversity
As an African-American with chronic illness, Eric Sibley prevailed in academic medicine where few colleagues shared his challenges.