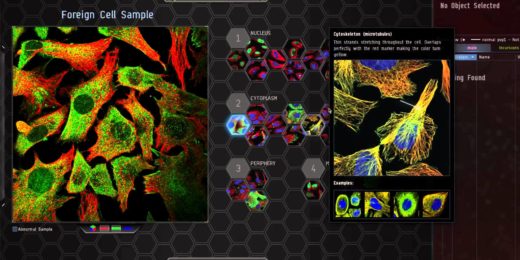
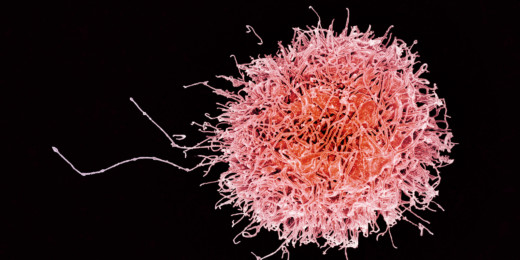
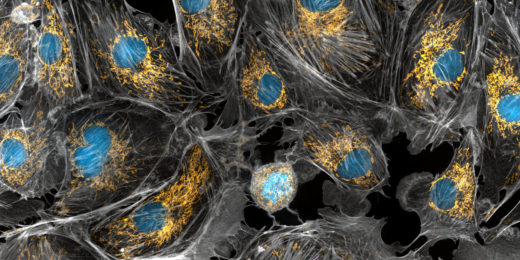
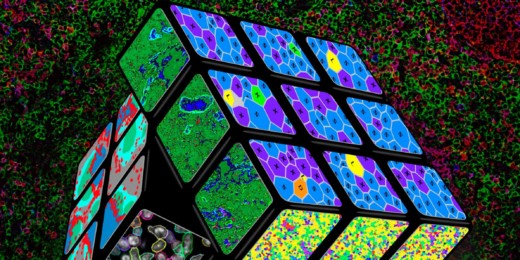
Citizen science through an online computer game, EVE online, helps scientists better classify protein locations inside a cell.
Category: Medical Research
Immune cell ratios predict shift to active tuberculosis, Stanford-led study finds
The ratio between a certain types of immune cells is able to predict whether latent TB will shift into an active infection, new research has found.
A closer look at the powerhouses of the cell, mitochondria
A recent lecture by clinician-researcher Daniel Bernstein highlighted an imaging technique for assessing the diverse ways mitochondria behave within heart cells.
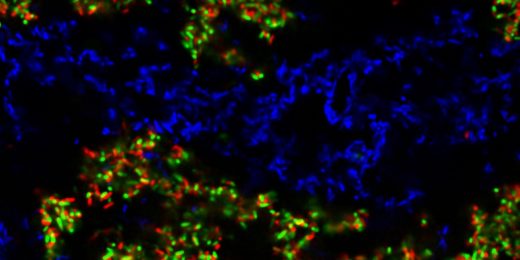
New technology provides a better understanding of cells and their neighbors
New technology developed at Stanford Medicine automatically identifies cell types and provides view of how cells interact with their environment.
Google Glass helps kids with autism understand faces, Stanford study finds
A pilot trial shows that equipping Google Glass with a face-recognition app can improve social skills in kids with autism.
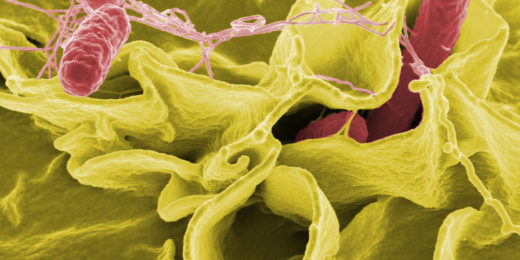
Some gut bacteria protect against Salmonella, new research suggests
Propionate molecules made by intestinal bacteria inhibits growth of Salmonella and may be a promising new treatment for gut infections.
Eavesdropping on elephants in the name of research
Adjunct Professor Caitlin O’Connell-Rodwell studies elephant vocalizations and vibrations to inform research on hearing, hearing loss and deafness.
How you get around depends on how fast you’re moving
How our brains blend cues from multiple senses to estimate our speed and position in space depends on where we are and how fast we seem to be moving.
Peering into reprogramming’s black box, Stanford researchers ID critical stem cell creation protein
Stanford researchers identify a new protein that can fully substitute for one of the key "Yamanaka factors" to reprogram adult stem cells.
Continuous blood sugar monitoring suggests even “healthy” people need to mind their carbs
Continuously monitoring blood sugar levels turns up new evidence to suggest that more people have sharp increases in their blood sugar than expected.
From AI to clinical informatics, Big Data conference videos offer deeper dive
Video interviews from Stanford's Big Data in Precision Health conference explore topics from artificial intelligence in radiology to clinical informatics.
Stitching single cells together any which way you want to
What if you could stitch together single cells any way you wanted to? Potential medical and even industrial applications abound.
Biodesign fellows simplify heart rhythm monitoring
A former Stanford biodesign innovation fellow describes how he and colleagues came to develop an inexpensive and simple tool to diagnose arrhythmias.
Scientists use magnets to detect cancer
A small magnetic wire that attracts nanoparticles engineered to stick to tumor cells may stand to detect cancer earlier.
Is nutrition research dependable? Stanford’s John Ioannidis weighs in
John Ioannidis recommends a change to the standards of nutrition research studies, suggesting that, as they stand, the results are fairly unreliable.
Stanford data analyst’s childhood inspires his research: A Q&A
Data analyst Jonathan Altamirano discusses living in Nicaragua as a child and how that inspired his current health research at Stanford.